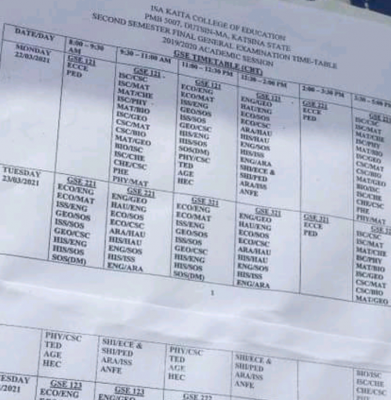
Those who are “business brilliant” have, on average, more failures than members of the middle-class. But they use those failures to help them succeed on the next attempt.
How many times has your success depended on knowing something that most people don’t? The survey research I did for my new book, Business Brilliant, uncovered just how frequently highly-successful people think and act differently from the great majority of people with identical levels of education and smarts.
There are certain elements of success that everyone agrees on–ambition, hard work, persistence, and a positive attitude. But my survey showed how some people have “business brilliance,” a distinctive take on getting ahead that is often at odds with the more pervasive mindset.
If you want to get an edge and separate yourself from the common herd, take some cues from the seven beliefs and habits of the most successful people:
1. An equity position is necessary to get wealthy.
Ninety percent of the super-successful say this is true, versus fewer than half of the masses. More importantly, 80 percent of “business brilliant” people say they already have an equity stake in their work. Just 10 percent of the middle-class have an equity position of any kind, and the vast majority (70 percent) say they’re not even trying to get one.
2. I’m always looking to gain an advantage in my business dealings.
About 90 percent of “business brilliant” individuals say they are always trying to grab an edge, compared with just about 40 percent of the middle-class. Gaining even small advantages in a series of deals can have a cumulative effect on your wealth, but since most people aren’t even looking for one, they’re that much more likely to end up on the disadvantaged side of every deal.
3. Doing things well is more important than doing new things.
Getting wealthy usually means you’ve taken an ordinary idea and executed it exceptionally well. That’s what 9 in 10 “business brilliant” people believe. Most other people, though, think that wealth requires a big, new idea. Unfortunately for them, big ideas are rare and risky. Too many people are waiting on the sidelines for the perfect big idea to come along, while the most successful people have jumped in the game, and busily honed their skills at execution.
4. I hire people who are smarter than I am.
Exceptional execution requires those who are business brilliant to focus on the two or three things they do very well. So they get their work done by building teams with complementary capabilities. Surveys show that most people, though, would rather learn to do tasks they’re bad at than get others to do them. The business brilliant know that you get to the top because of your strengths, not your weaknesses.
5. It’s essential I really understand my business associates’ motivations.
If you’re dependent on other talented employees, you’d best know what makes those talented people tick. That’s the belief of about seven in 10 people in my “business brilliant” cohort, compared with fewer than 20 percent of the middle-class. My survey suggests that your willingness and desire to really get to know and understand your business associates is a sure marker of success–and one that most people don’t have.
6. I can easily walk away from a deal if it’s not right.
The “business brilliant” know that bad deals, like bad marriages, can be painful–and costly. So if the deal on the table isn’t right, 71 percent say they have no problem cutting bait and moving on. Only about 22 percent of the middle-class say the same. Most people are willing to take their chances on deals that don’t seem right from the start, even though it’s less risky to walk away.
7. Setbacks and failures have taught me what I’m good at.
Those who are “business brilliant” have, on average, more failures than members of the middle-class. But they use those failures to help them succeed on the next attempt. Just 17 percent of the middle-class say they learn from their failures in this way, which is really a shame. Everything worth trying contains an element of risk, after all. If you fall on your face, you might as well learn from the experience to help you succeed on your next try.